In 1956, India was grappling with overwhelming developmental challenges – with a poverty rate of more than 50%, and a literacy rate of around 25%. Yet, that year, scientists from India’s Atomic Research Institute activated Apsara, the country’s first nuclear power reactor, in the coastal town of Tarapur. India’s efforts to develop sophisticated technology in the face of socio-economic challenges do not represent an odd juxtapositioning. Instead, these efforts are emblematic of India’s long-standing approach to harness science for the betterment of its people. In 1956, India needed cleaner, cheaper energy to help improve the standard of living for millions of people, as it does today. As on 2024, India has 24 nuclear reactors with a combined generating more than 33,000 million units of carbon free-energy. The country’s top five nuclear power plants are listed below.
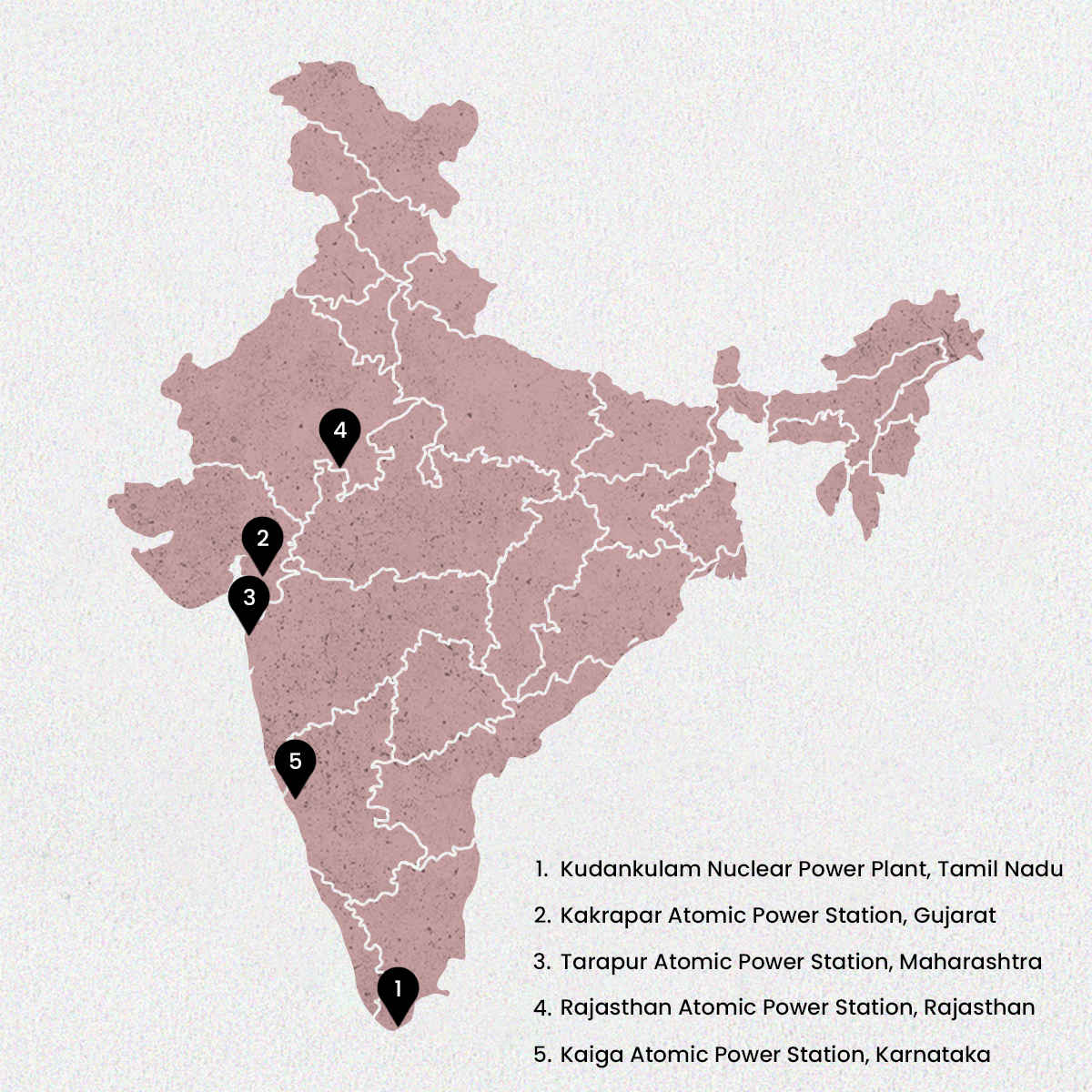
The Top 5 Nuclear Power Plants in India (based on installed generation capacity) are,
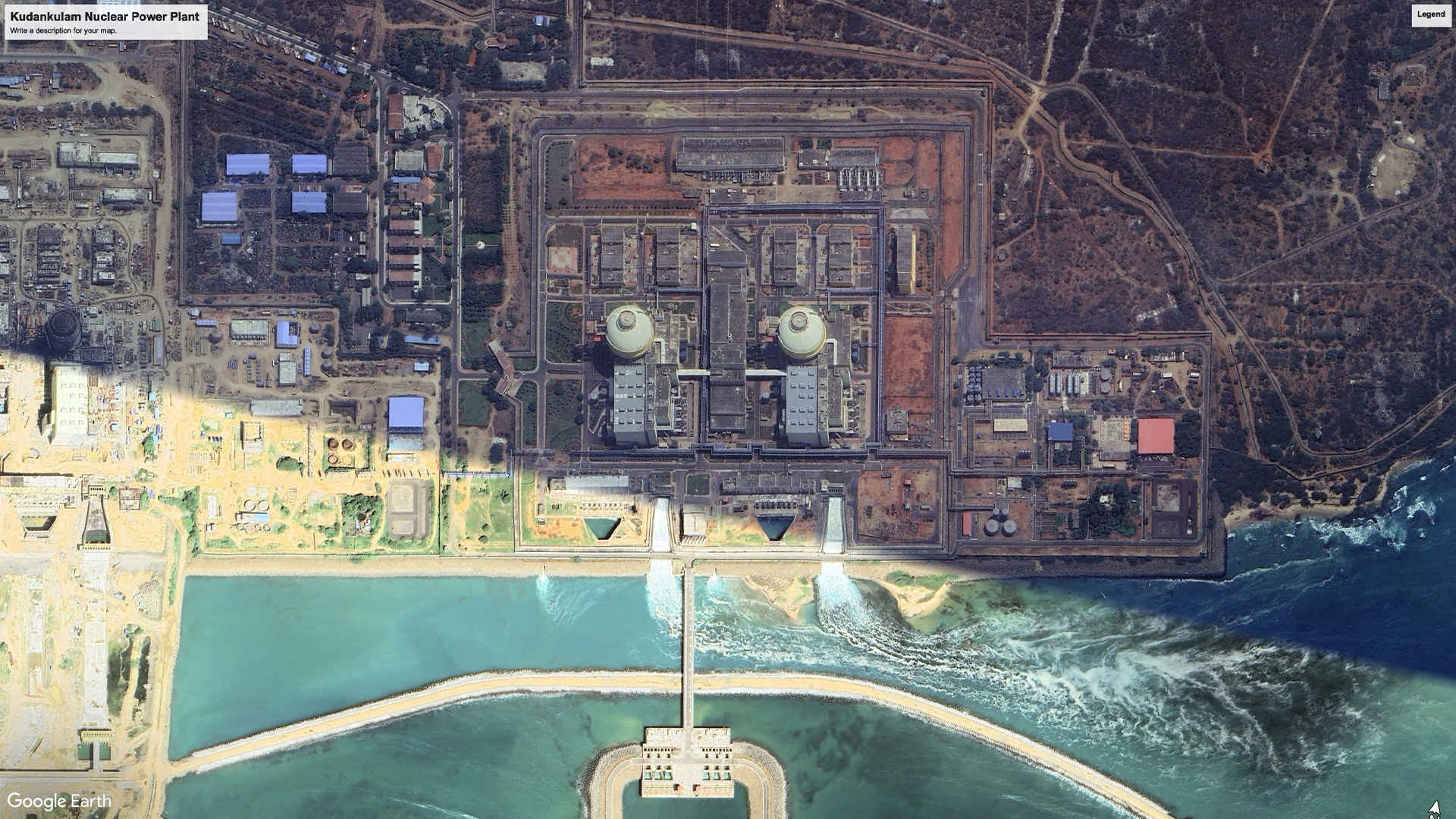
1. Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant, Tamil Nadu: 2000 MW (As on 2017)
India’s most ambitious nuclear power plant, Kudankulam currently runs two reactors of 1,000 MW capacity each, with four more on the way. Built in collaboration with the Russian atomic agency, Kudankulam has a dedicated port to allow easy movement of building and raw material for the plant.
Satellite Image, November 2024
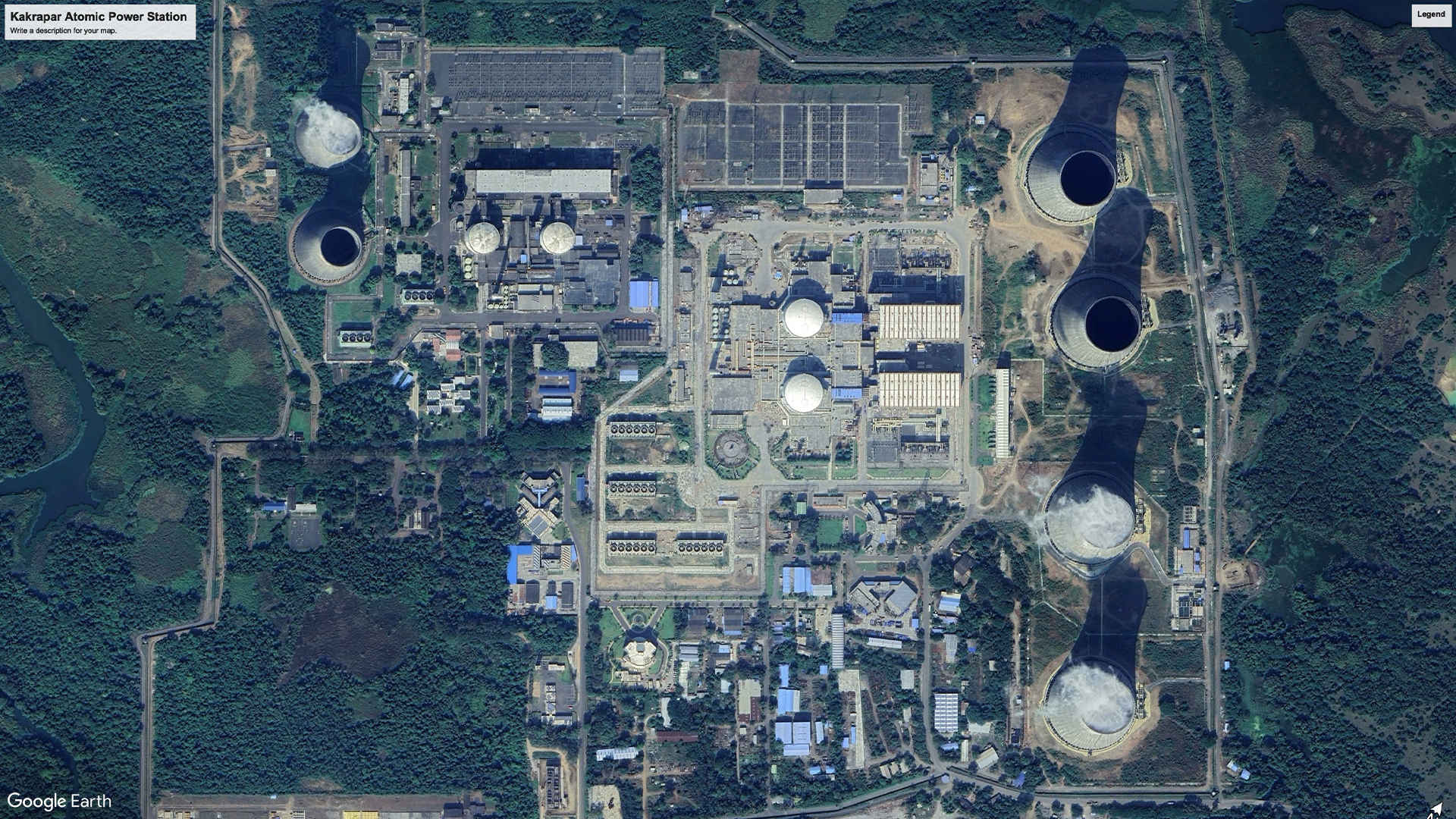
2. Kakrapar Atomic Power Station, Gujarat: 1840 MW (2023)
This power plant comprises four reactors built in two phases. The second phase, fully operational since early 2024, complements the first phase, which concluded in 1995. The plant's strategic location near Mandvi, Surat, and the Tapi River in Gujarat, coupled with its advanced remote-operated machine for fuel handling, enhances its efficiency and safety.
Satellite Image, November 2024
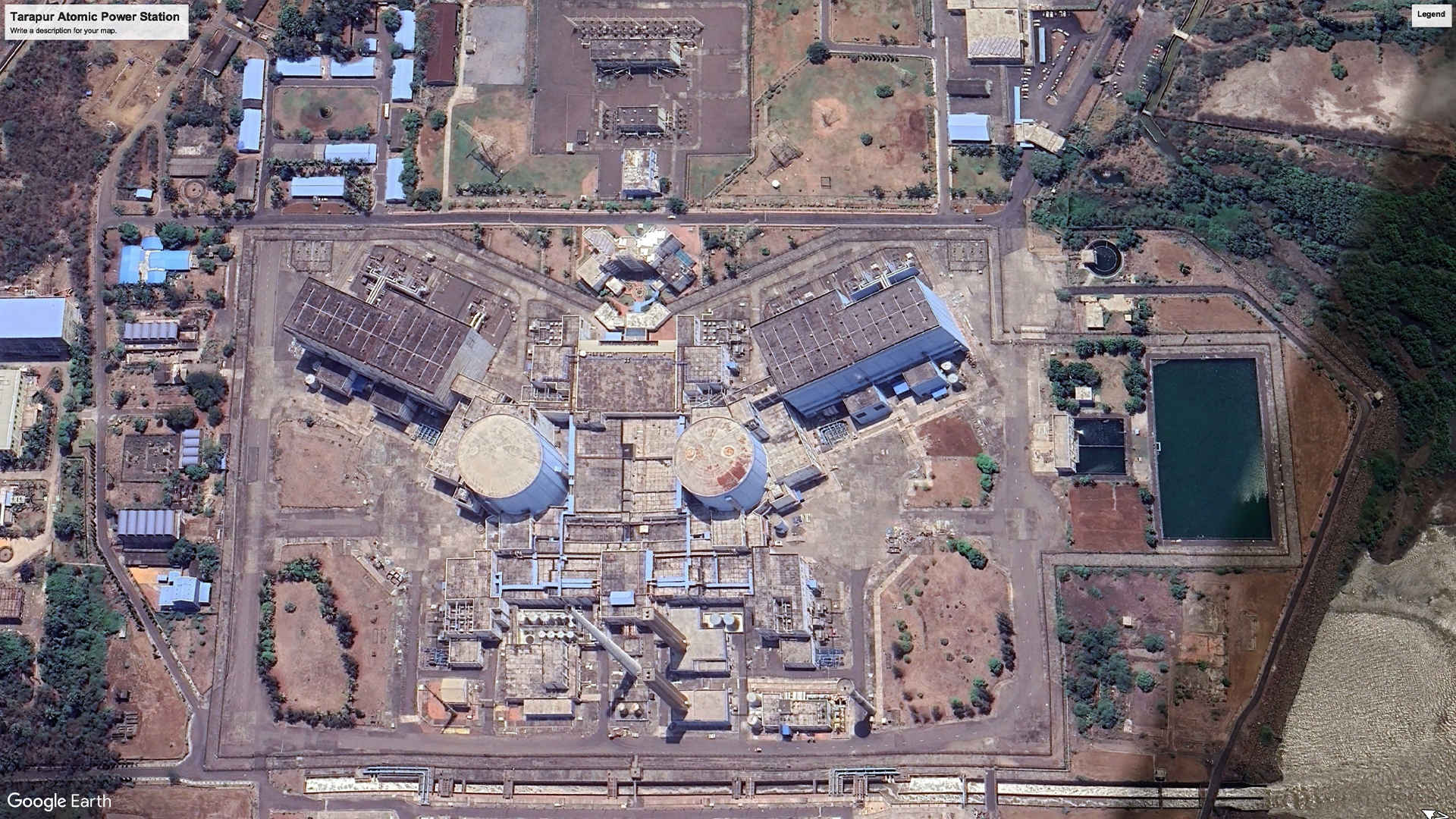
3. Tarapur Atomic Power Station, Maharashtra: 1400 MW (2006)
As India's inaugural nuclear power plant, Tarapur houses India’s only Boiling Water Reactors. While its first two reactors have been temporarily shut down for repairs since 2020, the second phase, completed in 2006, continues to contribute to the nation's energy needs.
Satellite Image, November 2024
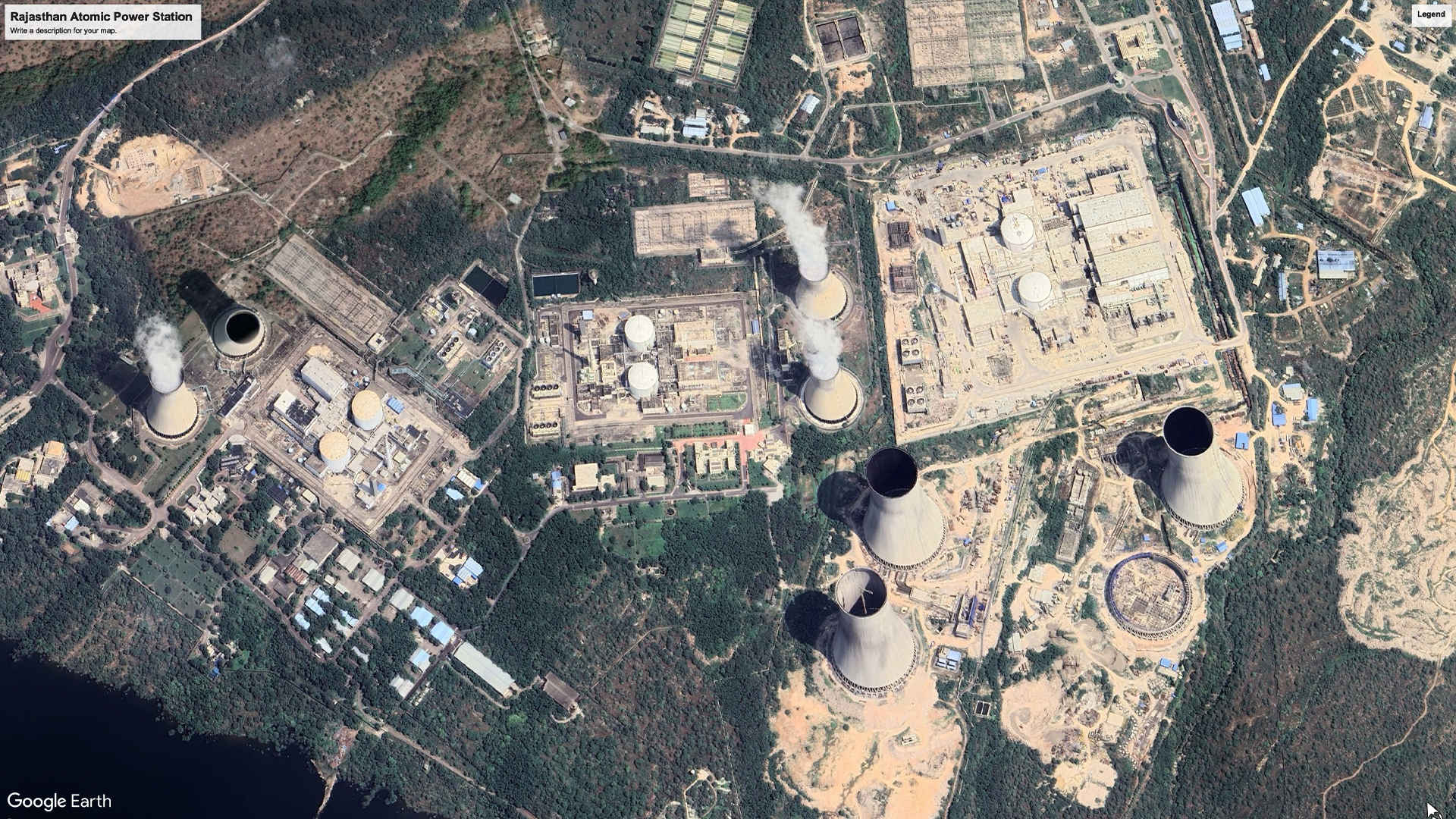
4. Rajasthan Atomic Power Station, Rajasthan: 1080 MW (2000)
Initially developed with Canadian support, the Rajasthan Atomic Power Station transitioned to indigenous development following India's 1974 nuclear weapons test. In 2024, the project’s 7th Unit, a 700 MW reactor, achieved criticality and is awaiting commercial operation, while Unit 8, also a 700 MW reactor, is in its final construction phase. A 2012 International Atomic Energy Agency audit recognized this nuclear power project as among the world's safest.
Satellite Image, November 2024
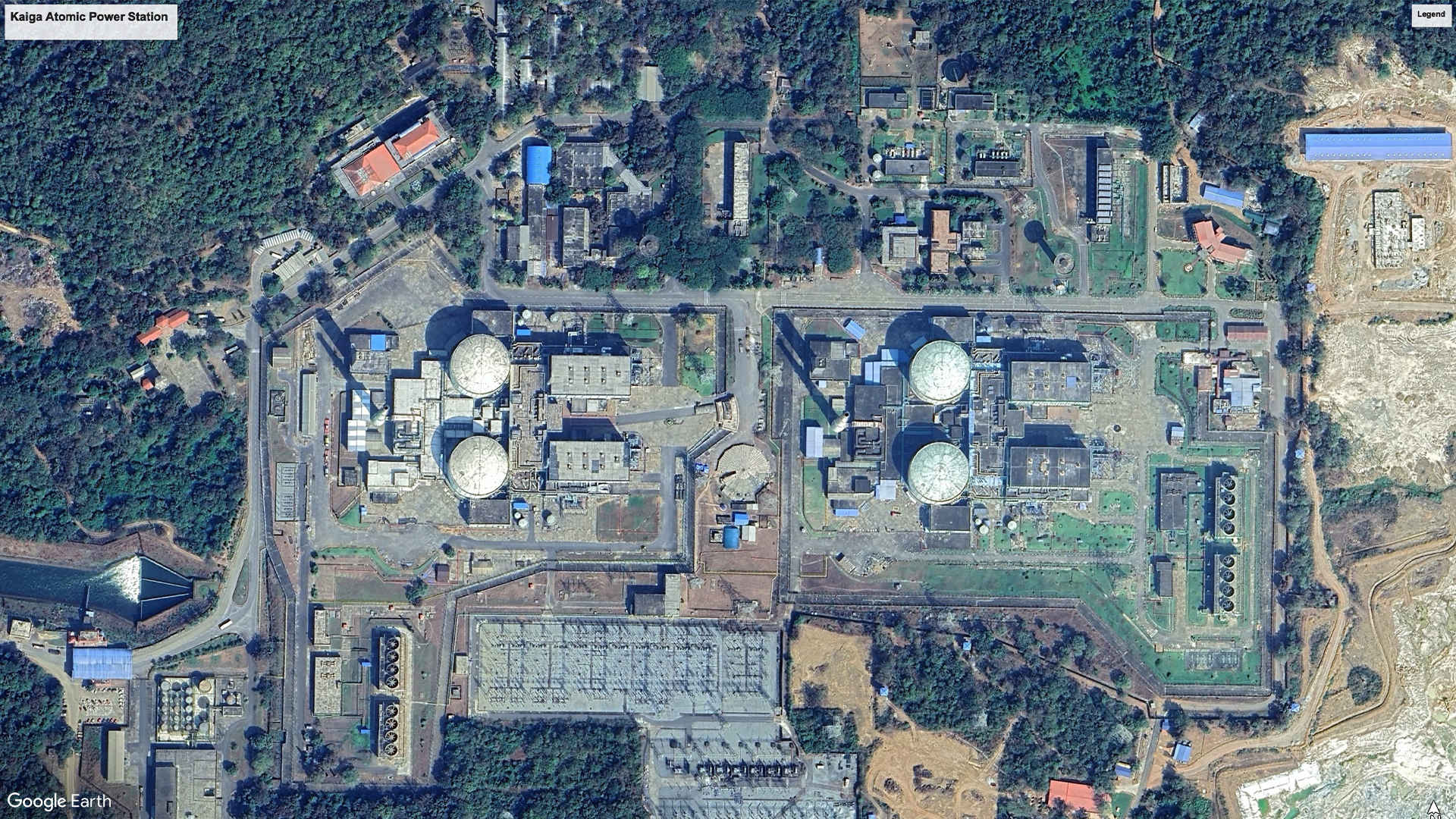
5. Kaiga Atomic Power Station, Karnataka: 880 MW (2011)
The Kaiga Atomic Power Station, situated on the Kadra Reservoir on the Kali River in Uttar (North) Karnataka, completed its second phase in 2011, following the first phase in 1999. With the ongoing construction of Kaiga 5 and 6, the plant's capacity is poised to increase to 2280 MW, solidifying its position as a significant contributor to India's nuclear power generation.
Satellite Image, November 2024
---